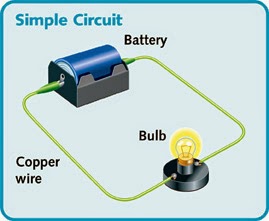
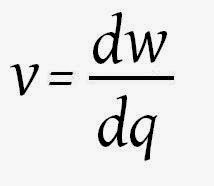Probably the most important
mathematical relationship between voltage, current and resistance in
electricity is something called “Ohm’s Law”. A man named George Ohm published
this formula in 1827 based on his experiments with electricity. As a school
teacher, Ohm began his research with the new electrochemical cell, invented by Italian
scientist Alessandro Volta. Using equipment of his own
creation, Ohm found that there is a direct proportionality between the
potential difference (voltage)
applied across a conductor and the resultant electric current.
This relationship is known as Ohm's law.
Ohm's
Law Formula / Equation
When we know the voltage and
resistance, we can calculate the current.
Ohm's
law definition
The resistor's current I in amps (A)
is equal to the resistor's voltage VR=V in volts (V) divided by the
resistance R in ohms (Ω):
V
is the voltage drop of the resistor, measured in Volts (V). In some cases Ohm's
law uses the letter E to represent voltage. E denotes electromotive
force.
I
is the electrical current flowing through the resistor, measured in
Amperes (A)
R
is the resistance of the resistor, measured in Ohms (Ω)
Voltage
calculation
When we know the current and
resistance, we can calculate the voltage.
The voltage V in volts (V) is equal
to the to the current I in amps (A) times the resistance R in ohms (Ω):
Resistance
calculation
When we know the voltage and the
current, we can calculate the resistance.
The resistance R in ohms (Ω) is
equal to the voltage V in volts (V) divided by the current I in amps (A):
Since the current is set by the
values of the voltage and resistance, the Ohm's law formula can show that:
- If we increase the voltage, the current will increase.
- If we increase the resistance, the current will reduce.
Learn more by watching this video:
“Invention is the most important product of man's creative brain. The
ultimate purpose is the complete mastery of mind over the material
world, the harnessing of human nature to human needs.”